
A nonprofit may be connected to a church, an alumni association, or clubs for children like Big Brothers Big Sisters or the Boys & Girls Club of America. Or a nonprofit may be championing a cause, like feeding the hungry, helping the homeless, providing https://www.bookstime.com/ affordable housing, fighting a particular disease, or any other good causes. Nonprofits operate for a variety of charitable reasons ranging from health care to education, from religion to advocacy, and from human services to animal rescue or care.
5 Nonprofits as Advocates and Adversaries to Government
This type of exempt status covers business leagues, real estate boards, professional associations and chamber-of-commerce or board-of-trade organizations. To qualify for 501(c)(6) status, the organization must be supported by membership dues and income related to its exempt purpose. The term is meant to describe a nonprofit organization not operating primarily to make a profit. Instead it an organization whose mission focuses on furthering a social cause or a shared goal or mission.

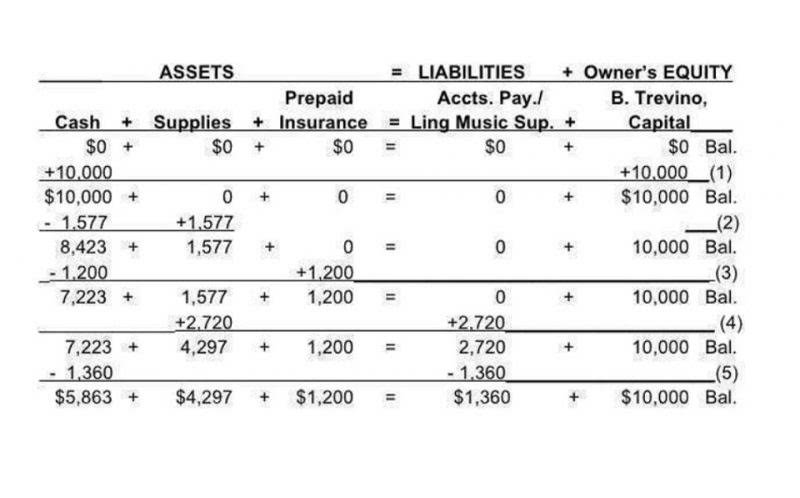
Big Differences between NPO and Government Accounting
For-profit organizations generate revenue by offering products or services to customers. Their income is subject to taxes, and profits can be distributed among shareholders or reinvested in the business. To ensure proper tax reporting and guarantee that you get the most value from volunteers, nonprofits must establish a system to track and record their work. Updating these records should be part of regular bookkeeping and accounting operations, and the financial tracking system should be standardized across the organization.
Government Regulations for Nonprofit Organizations
Many nonprofit organizations work closely with government at the federal, state and local level in the United States. International nonprofits may work closely with their own federal governments, the governments where they work or international agencies like the United Nations or International Monetary Fund. Alternatively, organizations may work in conflict with government(s) government and nonprofit accounting through their advocacy efforts. This chapter covers the different ways nonprofit organizations interact with government and government agencies, from close partners to adversaries. Both state and federal governments offer the reward of not having to pay taxes to non-profit organizations because of the help they provide and good they do in their local communities.
How Many Nonprofits Are In The United States?
- One of the most important aspects of running an organization is establishing a consistent method for funding projects and operations.
- At a nonprofit, leadership is often structured as a board of directors who gain no financial benefit from their governance role.
- A nonprofit organization or foundation (NPO), also known as a non-business entity, not-for-profit organization, or nonprofit institution, is dedicated to furthering a particular social cause or advocating for a shared point of view.
- With dozens of tax-exempt 501 statuses available, it can be difficult to choose the right nonprofit type for your organization.
- For example, many organizations meet the requirements that release temporarily restricted funds but don’t realize it because no one keeps track.
- Rather, this type of organization can only operate in compliance with the regulations set forth by the government in the form of state and federal laws and rules.
Governments treat our money in a distinctive way—they’re not trying to make a profit. Ideally, a government wants expenditures to be very close to revenue in any given year. Differences between revenues and expenditures are called surpluses (a positive difference) or deficits (a negative difference). Don’t forget, though, that a surplus is not a profit, nor is a deficit a loss—governments aren’t in the business of hoarding money (nor are they “in business” at all, as it were). Unlike a for-profit company, if a government finds itself operating at a large surplus (profit), it will usually take steps to lower the tax burden for its residents. As the public and nonprofit sectors rely on each other to provide services, understanding and improving their relationship is a high priority.
Private foundations conversely distribute money via grants to fulfill a public purpose. Private foundations are also not allowed to engage in direct lobbying activities. NGOs usually operate internationally and often have a centralized main office with satellite organizations reporting back to it. Nonprofits can be local, regional, or national in scope and are governed by a board of directors and headed by a CEO or Executive Director. A nonprofit organization is an entity that is created and operated for charitable or socially beneficial purposes rather than to make a profit.

- In contrast, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) oversees the financial reporting standards for nonprofit accounting.
- The government offers this tax break to promote the presence of organizations that exist purely for the public good and help them stay afloat.
- For many agencies such as the YMCA and the American Red Cross, the Community Chest quickly became a major source of revenue.
- Like NPOs, NGOs can receive tax exemptions by applying as a 503(c) type of business with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
- Some of these services are highly complex, involving many types of professionals and the legal system.
